Acne Treatments
How to Treat Acne: Effective Solutions for Clearer Skin
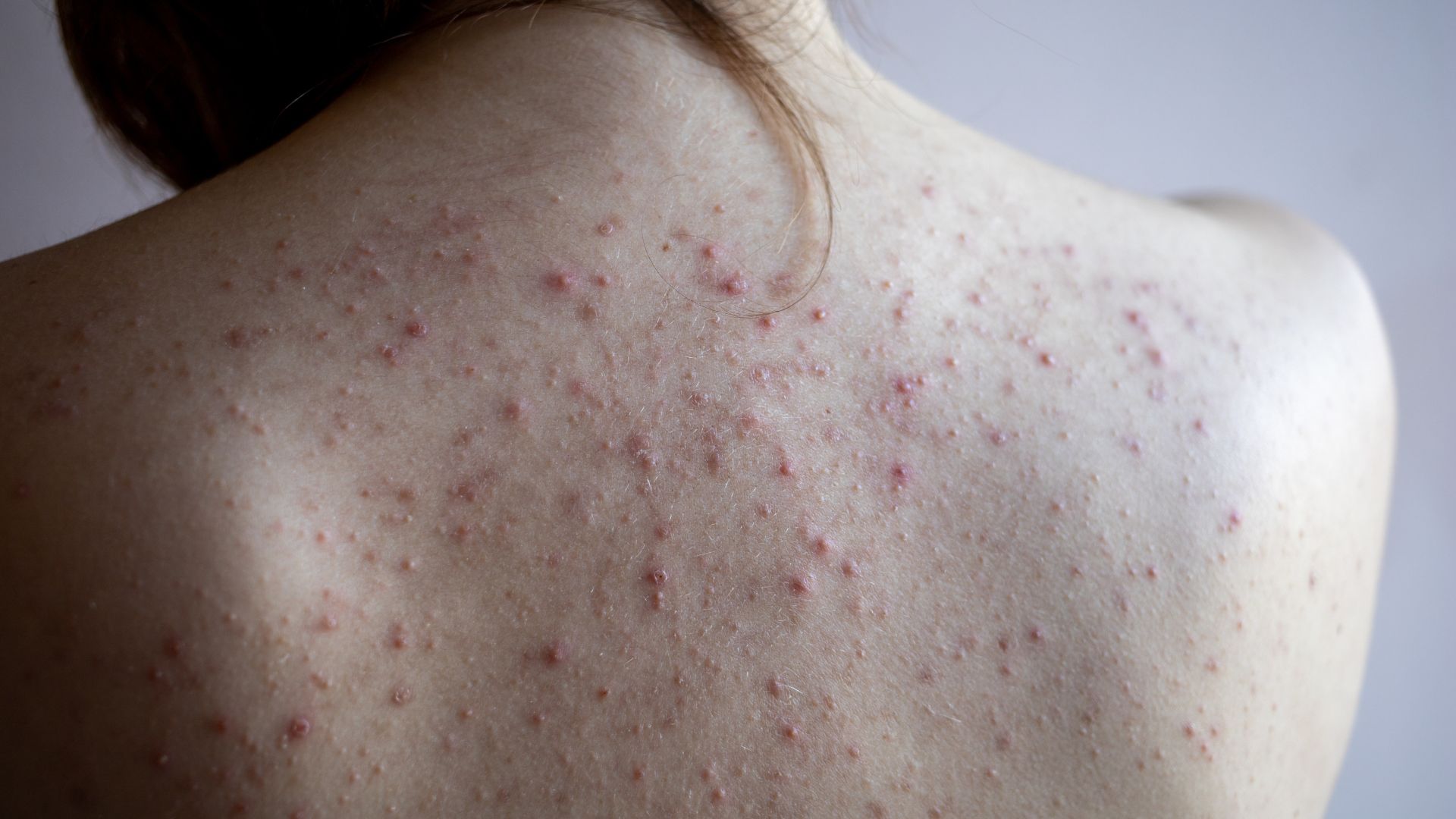
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, affecting millions of people of all ages. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria, leading to the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and in severe cases, cysts or nodules. While it can be frustrating and difficult to manage, there are several effective treatments that can help control and reduce acne, depending on the severity of the condition.
Effective Acne Treatments
1. Topical Treatments
Topical solutions are among the most common and effective first-line treatments for mild to moderate acne.
Benzoyl Peroxide: Known for its antibacterial properties, benzoyl peroxide helps reduce inflammation and kill acne-causing bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes). It also helps to dry out existing pimples and prevent new breakouts. It’s available in different strengths (from 2.5% to 10%) as gels, creams, and cleansers.
Salicylic Acid: This beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) works as an exfoliant, helping to unclog pores by removing dead skin cells and excess oil. Salicylic acid is particularly effective for blackheads and whiteheads.
Retinoids: Topical retinoids like adapalene or tretinoin are vitamin A derivatives that promote cell turnover, prevent clogged pores, and reduce inflammation. These are highly effective for treating and preventing breakouts, though they can cause initial dryness or irritation.
Azelaic Acid: An anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent, azelaic acid helps unclog pores and reduce bacteria on the skin. It’s especially beneficial for individuals with sensitive skin or post-acne hyperpigmentation.
2. Professional Treatments
For those seeking additional help, professional treatments can provide deeper and faster results, often in combination with topical or oral therapies.
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels with salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or lactic acid can help exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and reduce the appearance of post-acne marks. Professional peels are stronger than at-home versions, offering more dramatic results.
Laser Therapy and Light Treatments: Lasers and light-based treatments (like blue light therapy) target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation. These treatments can also help with acne scars and hyperpigmentation.
Corticosteroid Injections: For large, painful cysts, a dermatologist may inject a corticosteroid directly into the lesion to reduce swelling and speed up healing.
Extraction: A dermatologist can safely extract blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts to prevent further inflammation or infection. This should be done professionally to avoid scarring or further irritation.
Types of Acne
Understanding the type of acne you have is key to choosing the right treatment. The most common forms include:
- Comedonal Acne: This type includes blackheads and whiteheads caused by clogged pores.
- Inflammatory Acne: Pimples, red bumps, or pustules that are inflamed due to bacteria.
- Cystic or Nodular Acne: Severe, painful, and deep breakouts that can lead to scarring.
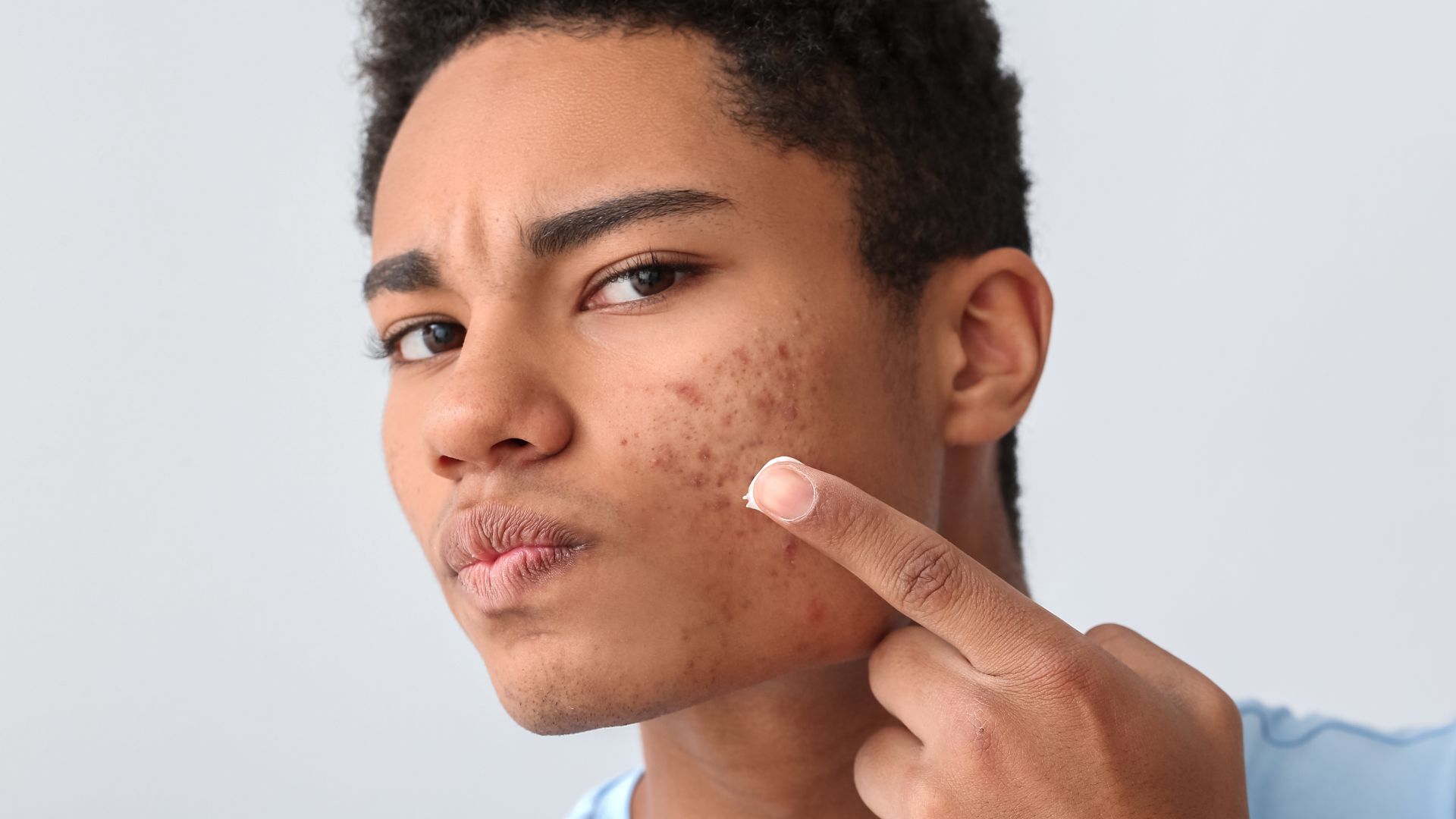

Treating acne requires a personalized approach based on the type and severity of the condition. From topical treatments like benzoyl peroxide and retinoids to oral medications and professional therapies, there are many effective options available. Consistency is key—finding the right combination of treatments and maintaining a gentle skincare routine can significantly improve acne and restore your confidence in your skin.
Reflections Laser & Aesthetics
1 (561) 221-1462.